Eastern hog-nosed snake
Heterodon platirhinos
Heterodon platirhinos
HARMLESS
Description:
This snake's most obvious feature is its pointed, upturned snout. It has a yellow to tan body color with dark blotches down its back and round spots along its sides. The underside of the tail is light and the anal plate is divided.
(Note: the hog-nosed snake with the dark coloration is melanistic, which means it has an increased amount of black pigmentation in its skin.)
Size:
Adults 20 - 40 inches (51 - 102 cm)
Prey:
Toads and frogs
Reproduction:
Mates in spring and lays 4 - 60 eggs, which hatch in mid-summer. Hatchlings are 6 - 9 inches (15 - 23 cm) long.
Habitat:
Wooded hillsides, fields, and sandy areas
Other Information:
This is the most dramatic of Oklahoma's snakes. Its defense lies not with biting, but rather with extreme bluffing. When molested it will spread out its neck and hiss. If this does not deter the predator, it will feign death. This includes rolling over on its back, going limp, and hanging its tongue out of its mouth. If righted, it will simply roll over on its back again and continue to play dead.
Commonly called a "spreading adder," the hog-nosed snake is not related to the true adders found on other continents, all of which are classified as venomous.
Hog-nosed snakes, while technically rear-fanged, do not have venom that's deadly to humans. Their saliva has been found to have some toxic properties, but only affects their prey, which is typically toads and frogs. Humans occasionally get bitten by hog-nosed snakes, and this generally occurs while feeding captive snakes. Symptoms often include skin irritation and some swelling.
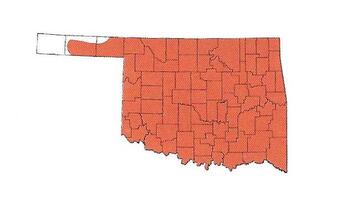
Why doesn't the range map show this species in my county?
Description:
This snake's most obvious feature is its pointed, upturned snout. It has a yellow to tan body color with dark blotches down its back and round spots along its sides. The underside of the tail is light and the anal plate is divided.
(Note: the hog-nosed snake with the dark coloration is melanistic, which means it has an increased amount of black pigmentation in its skin.)
Size:
Adults 20 - 40 inches (51 - 102 cm)
Prey:
Toads and frogs
Reproduction:
Mates in spring and lays 4 - 60 eggs, which hatch in mid-summer. Hatchlings are 6 - 9 inches (15 - 23 cm) long.
Habitat:
Wooded hillsides, fields, and sandy areas
Other Information:
This is the most dramatic of Oklahoma's snakes. Its defense lies not with biting, but rather with extreme bluffing. When molested it will spread out its neck and hiss. If this does not deter the predator, it will feign death. This includes rolling over on its back, going limp, and hanging its tongue out of its mouth. If righted, it will simply roll over on its back again and continue to play dead.
Commonly called a "spreading adder," the hog-nosed snake is not related to the true adders found on other continents, all of which are classified as venomous.
Hog-nosed snakes, while technically rear-fanged, do not have venom that's deadly to humans. Their saliva has been found to have some toxic properties, but only affects their prey, which is typically toads and frogs. Humans occasionally get bitten by hog-nosed snakes, and this generally occurs while feeding captive snakes. Symptoms often include skin irritation and some swelling.
Why doesn't the range map show this species in my county?